In a swirl of outrage, OpenAI claims DeepSeek is relying on its proprietary ChatGPT data to train its own AI products. The allegations are over what is called distillation, a technique that allows smaller models to learn from bigger ones simply by extracting knowledge. DeepSeek has not yet publicly responded to OpenAI’s claims about these accusations, which it claims has ‘solid evidence’ against.’
The issues of intellectual property rights, AI ethics and global AI competition that are raised by the controversy are of great importance. It has also raised questions about the necessary regulation to guarantee sane AI development practices, and this dispute has even inspired discussions about how to rectify these errors.
Table of Contents
OpenAI’s Accusations Against DeepSeek
DeepSeek, meanwhile, claims to be using distillation to get information about ChatGPT, an illegal use of their terms, OpenAI says. According to reports, Microsoft’s security researchers discovered unusual activity in late 2024 when they found that large amounts of data were being exfiltrated from OpenAI developer accounts. The activity was linked by Bloomberg sources to DeepSeek and triggered an ongoing investigation. This could have serious legal and financial consequences if the allegations turn out to be true for DeepSeek and other companies that follow a similar path of practice.
What is Distillation?
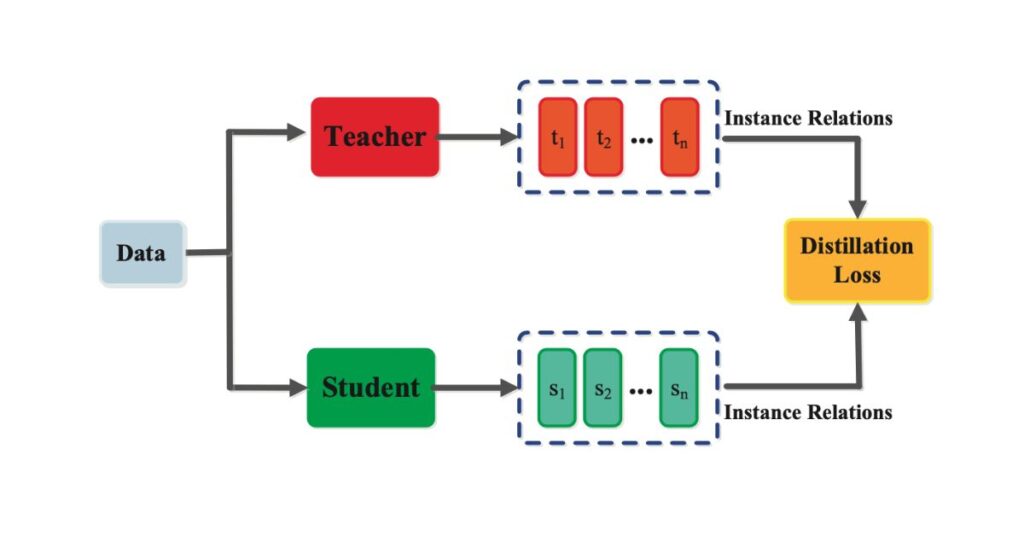
Distillation is a known AI training technique, which allows less powerful models to emulate the performance of more powerful ones while costing less. However, distillation itself is not illegal, but the use of it to clone proprietary AI models is prohibited by using it, OpenAI argues. The method consists of transferring the knowledge from a sophisticated AI to an inferior model while learning efficiently keeping performance.
Distillation is common use for AI companies to improve their models and OpenAI insisted that DeepSeek aked beyond ethical and legal lines by using unauthorized data extraction. GPT-4 is an openAI ‘s model, which reported to have cost over $ 100 million to develop, is one example of large scale AI investment that makes up controversy. If corporates are allowed to grab data from her proprietary models, it will negatively deter innovation and we’ll have unregulated chaotic AI industry where nobody knows who owns what, and there are no boundaries on assignment and usage.
DeepSeek’s Alleged Use of OpenAI’s Data
DeepSeek itself has not responded directly to these allegations — but some signs indicate that the chatbot it has put out to sea may have been trained on data from ChatGPT. Users also said that DeepSeek’s AI had also used terms referencing OpenAI and its policies and had inaccurately referred to itself as, “ChatGPT.” The presence of such errors implies a potential import of large amounts of information from ChatGPT to DeepSeek’s training data either intentionally or inadvertently by it.
Gregory Allen, an AI expert, said if DeepSeek had collected millions of interactions with ChatGPT for training, such anomalies could be explained. But he also said that chatting hallucinations are ubiquitous and these references alone can’t be taken as proof of hacked data. In addition, there has been no disclosure of concrete evidence regarding how DeepSeek allegedly got and used its proprietary data, allowing for debate over how significant the claim really is.
OpenAI’s Own History of Data Collection
OpenAI’s own practices also complicate the situation even further. In recent years, the company has been sued by media outlets, book authors and other content creators over unauthorized data scraping. OpenAI is hypocritical for this stance according to critics, as the very company that just recently incorporated DeepSeek acquired a lot of its training data from the public without explicit permission. It comes at a time when it seems unlikely that OpenAI has the power to define AI ethics, or whether it is simply acting out of self interest to preserve OpenAI’s competitive advantage.
Lutz Finger, an AI expert and lecturer at Cornell, noted that in spite of most terms of service agreements being violated, OpenAI itself has benefited using data sources which may or may not have been authorized. The issue is that there is no clear line between fair use and intellectual property theft when it comes to AI development, and he wanted to emphasize that.
The current debate brings to light the necessity to have clear and enforceable regulations that balance the innovative spirit with an adequate forum respecting intellectual property rights.
The Bigger Picture: China vs. the U.S. in AI Development
This dispute has wider significance as a proxy between U.S. and Chinese AI firms. Broadly, OpenAI’s concerns line up with U.S. efforts to ensure China doesn’t get its hands on the most advanced AI technology. Knowing that the government has closely monitored the progression of AI, they have placed restrictions on which high performance chips can be export to other countries, as well as investigated the possibility of foreign AI entities creating security threats.
As a true cost efficient AI solutions provider, DeepSeek has entered and positioned itself as a tough competitor among its meteors. The company does seem to have trained its flagship DeepSeek-V3 model for a comparatively paltry $5.6 million—a tiny fraction of what that went into developing ChatGPT and other leading AI chatbots. Due to this dramatic cost difference the DeepSeek team has been speculating whether it really did develop its model without relying on leveraging anything provided by OpenAI.
Additionally, DeepSeek’s speed of advancement in the AI space has also been raising eyebrows with analysts questioning whether its success is purely based on innovation or whether success has also been gained by shortcuts by using external data sources but no authorization to do so. DeepSeek also depends on U.S. chipmaker Nvidia’s AI chips. It was able to acquire 10,000 Nvidia chips, the most advanced AI chips, just before U.S. export restrictions took effect, even though U.S. export restrictions have prevented China from getting the most advanced chips.
It also raises questions about how the company has found a way to become competitive in AI when, reportedly, its hardware capacity is limited as well. DeepSeek’s rise in the AI sector is taking place amidst zeroing in on times which have become tense enough between China and the U.S. geopolitical tensions and scrutiny of his practices.
OpenAI’s Response and Possible Legal Action
In response, OpenAI said it is in contact with the U.S. government to prevent it from trying to take knowledge from the models without its permission. Industry experts say a lawsuit is likely to follow as OpenAI has not yet revealed whether it intends to sue DeepSeek. If OpenAI takes legal action, that would establish a precedent for other AI related intellectual property disputes in the future.
OpenAI’s key partner has also led a guard: Microsoft. The tech giant has been processing OpenAI’s models to identify and ban accounts where it has found evidence of distillation techniques in use. But that data can never be proven to be from the origin that it claims to be — and such restrictions are hard to enforce. There is no definitive evidence to build a strong legal case thus proving the source since it could be difficult to trace back AI generated content to its original source.
The Future of AI Regulation and Intellectual Property Rights
This case is an illustration of the increased demand for standardized laws on the development of AI as well as on the rights of intellectual property. The more powerful and more widely used AI gets, companies are left to negotiate the very complex landscape of ethical and legal issues. Lack of clear guidelines provides for disputes, such as this, leading to uncertainty for businesses and developers alike.
One possible way out may be to set some international AI governance standards that determine the permitted ways of training models and utilizing the data. Without guidelines, such disputes as the OpenAI-DeepSeek controversy will continue to arise as the competition across the world intensifies to develop the best and more advanced AI. Fair and transparent policies to support innovation, but protect intellectual property rights should be created by governments, tech companies and regulatory bodies.
Conclusion
The charges against DeepSeek are fraught with another major issue — intellectual property rights, data ethics and international fields of competition of artificial intelligence. Furthermore, the accusations claim that DeepSeek may have utilized the data of ChatGPT to train its own AI, yet a conclusive proof remains elusive. It also highlights the ethical inconsistency in the practice of AI development in OpenAI’s own history of data collection.
Given that investigations continue, this case will influence how AI companies protect intellectual property and get data in the future. Whether DeepSeek were guilty of any unethical conduct or just a successful swimmer in the race remains to be seen, but the outcome of this dispute could define the way in which AI is invented and regulated worldwide. This controversy goes far deeper than the two companies that were involved, and the ramifications run well beyond their involvement as well, leading to a conversation that is at the cusp of tech ethics, intellectual property and, I might add, fair competition in an unfettered tech landscape.
Recent Post : Lenovo Tab P11 : Price, Specs and Opinion
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
1. What is the issue that has been raised between DeepSeek and OpenAI?
DeepSeek has been accused by OpenAI of using a technique known as distillation to extract knowledge from its ChatGPT model without authorization. The concerns here were raised about intellectual property theft and AI ethics.
2. What is AI distillation, and why have people been criticising it?
AI distillation is the method of parroting an experienced model’s reactions in smaller form. While this technique is widespread, OpenAI says DeepSeek broke its terms of service by using it to steal from proprietary ChatGPT data.
3. Does OpenAI have a proof that DeepSeek copied ChatGPT?
OpenAI has suggested there is evidence, but not disclosed details. DeepSeek’s chatbot would confuse itself for ‘ChatGPT’, according to some users and fuel speculation it was trained to work with ChatGPT generated data.
4. How DeepSeek has responded to these allegations.
OpenAI’s accusations against DeepSeek have not been officially answered by DeepSeek. Still, the company says it has built its models on open source AI and from companies such as Meta and Alibaba.
5. Have OpenAI been accused of using similarly caused data misuse?
OpenAI is definitely being accused of scraping data from media outlets and book authors as it shouldn’t be doing so. OpenAI’s stance regarding its data collection practices is hypocritical, critics say, considering that OpenAI is collecting data.
6. What legal consequences exist from this dispute?
If OpenAI proves that DeepSeek was in violation of intellectual property laws, it may seek legal action in bringing precedent for disputes involving intellectual property involving AI. Yet, proving AI training data origins is hard.
7. What is the reason for the U.S. government being a party in this case?
The U.S. government is paying very close attention to China’s progress in AI, and their own. This is consistent with broader attempts to block the circulation of high-performance AI technology and steal IP.
8. How does DeepSeek have the ability to create AI models at this low cost?
According to DeepSeek, it has trained its AI model for $5.6 million, the fraction of the price of OpenAI’s ChatGPT model. That has raised questions about whether it tried to do this without authorization or used cost effective methods of training.
9. How does this controversy affect the interests of a global AI competition?
It illustrates the rivalry between U.S. and Chinese AI firms. OpenAI’s accusations, if substantiated, could lead to stricter regulations and create tensions between governments and AI firms.
10. How would this affect AI regulation in the future?
The point of the case is that we need clear policies about use of data, model training and intellectual property on AI. In future disputes could governments and tech companies push for international standards to preclude such disputes.




Pingback: O3-mini : ChatGPT's New Model